Briefly Describe the Concept of Action Potential.
Using concepts of resting membrane potential depolarization and repolarization describe the events that occur on the muscle membrane sarcolemma in terms of aMotor end plate with ACh receptor. The action potential is the nerve impulse.
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart Membrane Potential Molecular Devices
Think of the gunpowder analogue again but this time coat the rod with some insulation and put gunpowder only at the bare regions.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)
. In the simplest sense action potential can be described as short electrical pulses that are created inside the cell body of the neuron. As the action potential begins its travel down the axon the sodium channels. Action potentials are caused when different ions cross the neuron membrane.
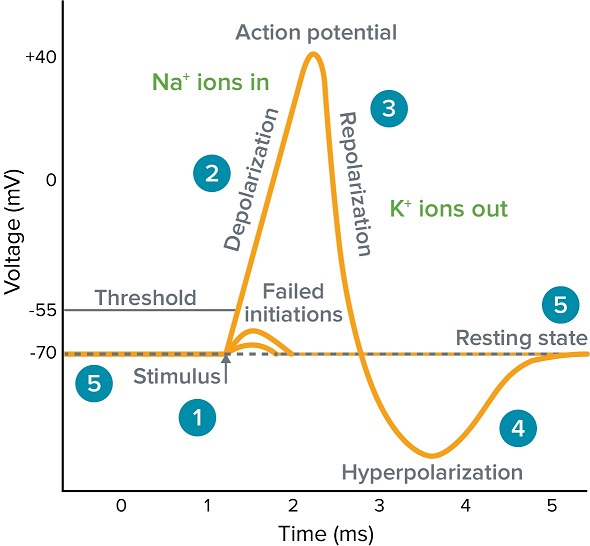
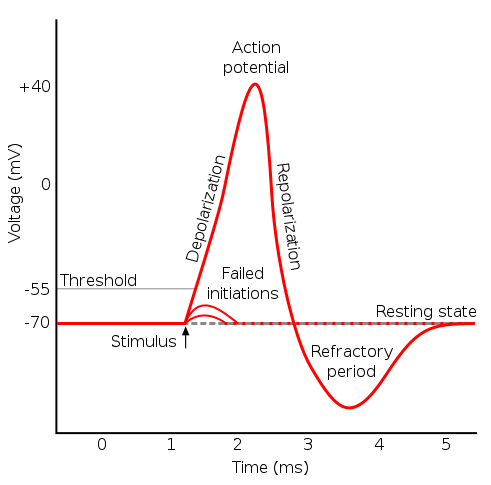
This process which occurs during the firing of the neurons allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon a portion of the neuron that carries nerve impulses. The cardiac cell action potential like action potentials in nerves is divided into five phases numbered 0 through 4. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 1257.
A rapid change in the membrane potential depolarization followed by a return to the resting membrane potential. It is a nongraded all-or-none event meaning that the magnitude of the action potential is independent of the strength of the depolarizing stimulus that produced it provided the depolarization is sufficiently large to reach threshold. Terms in this set 47 Define Action potential.
Sodium potassium and calcium are the primary ions. A stimulus first causes sodium channels to open. This concept can also be used to explain problems with conduction system such as in people with Arrhythmias.
Two of these phase 2 the plateau phase and phase 4 the diastolic interval are marked by little to no change in voltage. The action potential propagates down the axon away from the cell body. Propagation as described above applies to unmyelinated axons.
When myelination is present the action potential propagates differently. The action potential and consequent transmitter release allow the neuron to communicate with other neurons. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential.
Functions of Action Potentials 2 Basis of signal transmission of excitable cells nerve muscle and Initiation of muscle contraction. Action potentials - the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a nerve cell. An action potential travels the length of the axon and causes release of neurotransmitter into the synapse.
The action potential must propagate toward the axon terminals. Once an action potential is triggered the membrane potential goes through a stereotypical sequence of. Action potential Brief 1 ms electrical event typically generated in the axon that signals the neuron as active.
Calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Depolarization of membrane potential exceeds critical threshold -60mV 2. Please mark me as brainliest.
When neurons transmit signals through the body part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential. A neuron a nerve cell is the basic building block of the nervous system. Cardiac action potentials differ from the APs found in other areas of the body.
Typical neural AP duration is around 1ms and those of skeletal muscle are roughly 2-5ms whereas cardiac action potentials range from 200-400ms. The concept of cardiac action potential does not only helps us understand electrophysiologic mechanisms taking place in the heart. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication.
Binding of ACh with ACh receptor. The stimulus for this action potential is the depolarization that emerges from the end of the myelin. The change in the membrane voltage from -70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change.
Because there are many more sodium ions on the outside and the inside of the neuron is negative relative to the outside sodium ions rush into the neuron. The neurotransmitters that are excitatory release from the vesicles of the pre-synaptic membrane and enter into the post-synaptic membrane. As a result the polarity of the neuron is maintained as mentioned above.
Describe the relationship between the two. It consists of a wave of electrical depolarization that reverses the potential difference across the nerve cell membrane. It helps organisms to quickly adapt to an adverse circumstance that could have the potential to cause bodily harm or even death.
An action potential is defined as a sudden fast transitory and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. As the potential spreads outward from the trunk of the axon no voltage-gated channels are found toward the cell body so only potential changes flowing away from the cell body encounter excitable membrane. Describe the sequence of Na voltage-gated channel in a fast inactivation of an action potential.
Describe in as much detail as you can the concept of Action Potential1 how the decision for an individual neuron to âœfireâ is made2 once the decision is made what changes occur in the membrane of the neuron3 what changes occur with regard to specific ions4 how does this related to information transfer between neurons briefly. The generation of an action potential by the post-synaptic membrane occurs through a sequential process with the involvement of different neurotransmitters and ligand-gated ion channels. Nerve impulses - signals transmitted along a nerve fiber.
Action potential generation on sarcolemma. That property is called the excitability. Action potential is an event that happens between neurons in order to send messages from the brain to the different parts of the body whether for voluntary or involuntary actions.
For example an action potential and maximal twitch of muscle fibers is elicited when 013 of the total number of receptors at a skeletal neuromuscular junction is simultaneously activated. Each node acts as a relay station that renews the decremented signal. Transient brief 1ms-100ms depolarization of resting membrane potential due to opening of Na channels and Na influx.
Pulling our hands away immediately after touching a hot or cold object is a classic example of a reflex action. Nervous and muscle cells as well as non-pacemaker cardiac cells use the opening of Na channels to facilitate the depolarisation phase whereas cardiac. The concept of spare receptors explains a maximum response being achieved when only a fraction of the total number of receptors is occupied.

12 5 The Action Potential Anatomy Physiology
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology
0 Response to "Briefly Describe the Concept of Action Potential."
Post a Comment